目標
在本教程中,您將學習如何使用重建 API 進行稀疏重建
- 載入包含影像路徑列表的檔案。
- 執行 libmv 重建流程。
- 使用 Viz 顯示獲得的結果。
程式碼
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
static void help() {
cout
<< "\n------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n"
<< " 這個程式展示了 OpenCV 運動結構 (SFM) 模組中的多檢視重建能力。\n"
<< " 它可以從一組 2D 影像重建場景\n"
<< " 用法:\n"
<< " example_sfm_scene_reconstruction <檔案路徑> <f> <cx> <cy>\n"
<< " 其中:檔案路徑是系統中包含的檔案的絕對路徑\n"
<< " 用於重建的影像列表。\n"
<< " f 是焦距,以畫素為單位。\n"
<< " cx 是影像主點的 x 座標,以畫素為單位。\n"
<< " cy 是影像主點的 y 座標,以畫素為單位。\n"
<< "------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n\n"
static int getdir(const string _filename, vector<String> &files)
<< endl;
}
ifstream myfile(_filename.c_str());
{
if (!myfile.is_open()) {
cout << "無法讀取檔案: " << _filename << endl;
} else {;
exit(0);
size_t found = _filename.find_last_of("/\\");
string line_str, path_to_file = _filename.substr(0, found);
while ( getline(myfile, line_str) )
files.push_back(path_to_file+string("/")+line_str);
int main(
int argc,
char* argv[])
}
return 1;
}
// 讀取輸入引數
{
// 解析影像路徑
{
help();
exit(0);
}
getdir( argv[1], images_paths );
// 構建內參
cx = atof(argv[3]), cy = atof(argv[4]);
0, f, cy,
bool is_projective = true;
0, 0, 1);
vector<Mat> Rs_est, ts_est, points3d_estimated;
reconstruct(images_paths, Rs_est, ts_est, K, points3d_estimated, is_projective);
// 列印輸出
cout << "重建結果: " << endl;
cout << "============================" << endl;
cout << "估計的 3D 點: " << points3d_estimated.size() << endl;
cout << "估計的相機: " << Rs_est.size() << endl;
cout << "精煉的內參: " << endl << K << endl << endl;
cout << "3D 視覺化: " << endl;
cout << "估計的 3D 點: " << points3d_estimated.size() << endl;
window.setWindowSize(
Size(500,500));
window.setWindowPosition(
Point(150,150));
window.setBackgroundColor();
// 建立點雲
// 恢復估計的 points3d
for (int i = 0; i < points3d_estimated.size(); ++i)
point_cloud_est.push_back(
Vec3f(points3d_estimated[i]));
cout << "[完成]" << endl;
cout << "正在恢復相機 ... ";
vector<Affine3d> path;
for (size_t i = 0; i < Rs_est.size(); ++i)
path.push_back(
Affine3d(Rs_est[i],ts_est[i]));
if ( point_cloud_est.size() > 0 )
cout << "正在恢復相機 ... ";
cout << "正在渲染點 ... ";
{
viz::WCloud cloud_widget(point_cloud_est, viz::Color::green());
window.showWidget("point_cloud", cloud_widget);
cout << "無法渲染點:空點雲" << endl;
cout << "正在恢復相機 ... ";
}
else
{
if ( path.size() > 0 )
}
cout << "正在渲染相機 ... ";
{
window.showWidget(
"cameras_frames_and_lines",
viz::WTrajectory(path, viz::WTrajectory::BOTH, 0.1, viz::Color::green()));
window.setViewerPose(path[0]);
cout << "無法渲染相機:空路徑" << endl;
cout << "正在恢復相機 ... ";
}
else
{
cout << endl << "按 'q' 關閉每個視窗 ... " << endl;
}
window.spin();
cv::Affine3
return 0;
}
定義 affine.hpp:127
cv::Matx< double, 3, 3 >
用於指定影像或矩形大小的模板類。
Definition types.hpp:335
此 3D 小部件表示軌跡。
定義 viz3d.hpp:68
點雲.
Definition widgets.hpp:681
定義 widgets.hpp:628
定義 widgets.hpp:605
從 2d 對應點重建 3d 點,同時執行自校準。
定義 conditioning.hpp:44
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
定義 highgui_qt.cpp:3
首先,我們需要載入包含影像路徑列表的檔案,以便為重建 API 提供資料
/home/eriba/software/opencv_contrib/modules/sfm/samples/data/images/resized_IMG_2889.jpg
/home/eriba/software/opencv_contrib/modules/sfm/samples/data/images/resized_IMG_2890.jpg
/home/eriba/software/opencv_contrib/modules/sfm/samples/data/images/resized_IMG_2891.jpg
/home/eriba/software/opencv_contrib/modules/sfm/samples/data/images/resized_IMG_2892.jpg
int getdir(const string _filename, vector<string> &files)
...
string line_str;
{
if (!myfile.is_open()) {
cout << "無法讀取檔案: " << _filename << endl;
} else {;
exit(0);
} else {
files.push_back(line_str);
files.push_back(path_to_file+string("/")+line_str);
其次,構建的容器將用於為重建 API 提供資料。重要的是要指出,估計的結果必須儲存在 vector<Mat> 中。在這種情況下,呼叫的是真實影像的過載簽名,它從影像中內部提取和計算稀疏 2d 特徵,使用 DAISY 描述符,以便使用 FlannBasedMatcher 進行匹配並構建軌跡結構。
}
return 1;
}
reconstruct(images_paths, Rs_est, ts_est, K, points3d_estimated, is_projective);
vector<Mat> Rs_est, ts_est, points3d_estimated;
reconstruct(images_paths, Rs_est, ts_est, K, points3d_estimated, is_projective);
最後,獲得的結果將顯示在 Viz 中。
cout << "重建結果: " << endl;
cout << "============================" << endl;
cout << "估計的 3D 點: " << points3d_estimated.size() << endl;
cout << "估計的相機: " << Rs_est.size() << endl;
cout << "精煉的內參: " << endl << K << endl << endl;
cout << "3D 視覺化: " << endl;
用法和結果
為了執行此示例,我們需要指定影像路徑檔案的路徑、相機的焦距以及中心投影座標(以畫素為單位)。
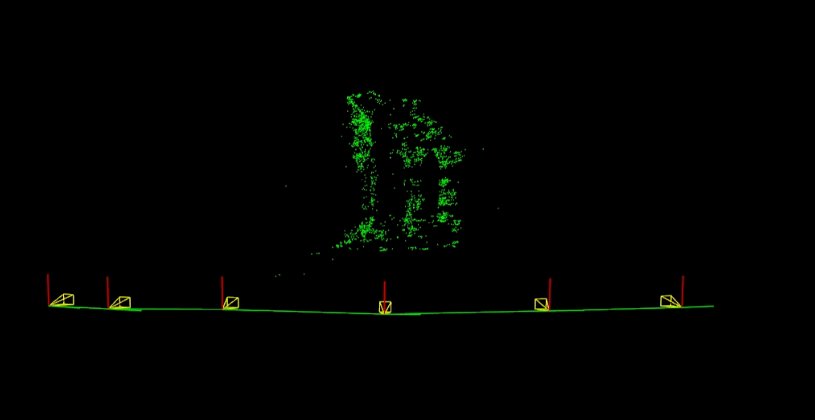
1. Middlebury 神廟
使用以下影像序列 [1] 和以下相機引數,我們可以計算稀疏 3d 重建
./example_sfm_scene_reconstruction image_paths_file.txt 800 400 225
下圖顯示了獲得的相機運動以及估計的稀疏 3d 重建
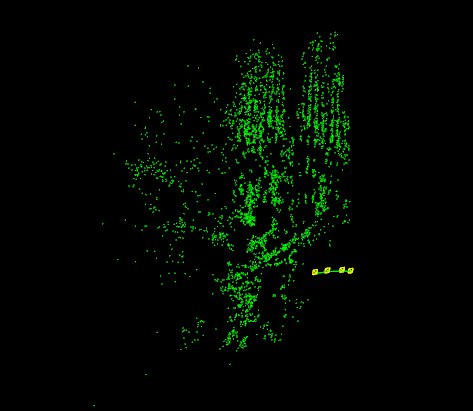
2. 聖家堂
使用以下影像序列 [2] 和以下相機引數,我們可以計算稀疏 3d 重建
./example_sfm_scene_reconstruction image_paths_file.txt 350 240 360
2. 聖家堂
[2] Penate Sanchez, A. and Moreno-Noguer, F. and Andrade Cetto, J. and Fleuret, F. (2014). LETHA: Learning from High Quality Inputs for 3D Pose Estimation in Low Quality Images. Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D vision (3DV). URL
生成於 2025 年 7 月 3 日星期四 12:14:36,適用於 OpenCV,作者: 1.12.0